MRP glossary TOP > Production Planning > Bill of Materials
Bill of Materials
There are various kinds of items such as parts and raw materials necessary to manufacture products in a factory. A bill of materials refer to the list where the relationships among items (e.g. product and its assemblies, assemblies and their parts, parts and their raw materials) are indicated. Focusing on how to maintain the data, the bill of materials can be divided into Product Summary B/M and Product Structure B/M, while in terms of how to use it, it can be divided into Engineering Bill of Materials, Production Bill of Materials, Planning Bill of Materials, Spare Bill of Materials, and etc. Moreover, according to how to express it, there are Single Level Bill of Materials, Indented Bill of Materials, and Summarized Bill of Materials.
A bill of materials is generally called B/M for short, and the list to display it is called Parts List. Speaking of B/M, it often refers to the master data in the Parts List. The B/M is expressed by two master data (item data and product structure data) in order to show the relationship between parent items and child items.
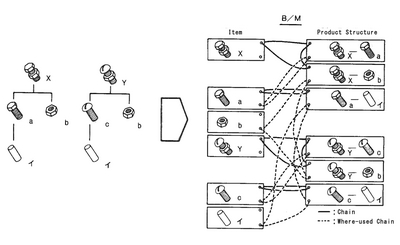
- Item data:
- It is the data in which the information unique to an item (e.g. products, assemblies, parts, raw material) is unified, and it consists of item number, item name, lead time, etc.
- Product structure data:
-
It is the data in which the information determined by the relationship between parent items and child items is unified, and it consists of parent item number, child item number, physical unit, etc.
The B/M created based on the above mentioned data is used by most of divisions in the manufacturing company. For example, in the engineering division, it is used to grasp the influence of engineering of the similar products or engineering change, and in the production technology division, it is used to review the routings and lead time. In addition, in MRP, the B/M is used to plan the logistics for parts and materials. The B/M is mainly used as follows:
Related term: Explosion method
Reference:JIT Business Research Mr. Hirano Hiroyuki
Backlog of Orders | Production Planning | Continuous Production
