MRP glossary TOP > Material Planning > Net Change
Net Change
Net Change
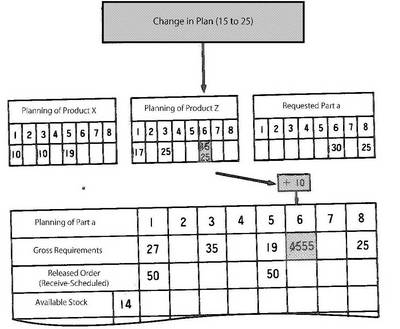
In MRP two types of operation methods are employed: one is to enter all production plans ever time and the other is to enter only difference between the previous plan and the latest one. The former is called Reschedule Planning, while the latter is called Net Change. In net change method, only difference between the previous plan and the latest one is handled by MRP. For example, in the figure, when the requirements 15 for Period 6 of Product Z 's production plan is changed to 25, only 10 (the difference from the previous requirements 15) is entered as net change to MRP. Many companies are now considering this method's employment as their future operation.
Compared with Reschedule Planning requiring all items' entry every handling, this method can make each MRP's processing time shorter, resulting in more frequent MRP's implementation. In Reschedule Planning, daily changes and planning additions are usually accumulated for a certain period and they are handled by MRP once a week or month. In this case, unlike in Net Change, Daily handling is difficult for its time. Thus Net Change is very suitable for the quick response to frequent plan changes in high-mix low-volume production. But it has still many problems to be solved, such as accumulated mistakes caused by the fact that whole of plan is not re-scheduled, mass data to be maintained, and difficult operation.
Antonyms: Regeneration
In MRP two types of operation methods are employed: one is to enter all production plans ever time and the other is to enter only difference between the previous plan and the latest one. The former is called Reschedule Planning, while the latter is called Net Change. In net change method, only difference between the previous plan and the latest one is handled by MRP. For example, in the figure, when the requirements 15 for Period 6 of Product Z 's production plan is changed to 25, only 10 (the difference from the previous requirements 15) is entered as net change to MRP. Many companies are now considering this method's employment as their future operation.
Compared with Reschedule Planning requiring all items' entry every handling, this method can make each MRP's processing time shorter, resulting in more frequent MRP's implementation. In Reschedule Planning, daily changes and planning additions are usually accumulated for a certain period and they are handled by MRP once a week or month. In this case, unlike in Net Change, Daily handling is difficult for its time. Thus Net Change is very suitable for the quick response to frequent plan changes in high-mix low-volume production. But it has still many problems to be solved, such as accumulated mistakes caused by the fact that whole of plan is not re-scheduled, mass data to be maintained, and difficult operation.

Antonyms: Regeneration
Reference:JIT Business Research Mr. Hirano Hiroyuki
